News Center
What are the Advantages of Laser Cutting?
In today's fiercely competitive market, manufacturers constantly seek ways to enhance work efficiency and guarantee product quality. Choosing the right metal cutting technology is paramount to achieving these goals and gaining a significant edge. While various methods exist, laser cutting technology stands out with a unique set of advantages that can transform your production capabilities.
If you're considering upgrading your equipment or exploring options beyond traditional methods like plasma cutting, understanding why laser cutting is often the preferred choice is crucial. It's not just another way to cut metal; it's a strategic investment in precision, speed, and versatility.
Why Laser Cutting Wins: The Competitive Advantages
Choosing a laser cutting system is a deliberate move towards superior performance. Here’s what makes this technology so compelling:
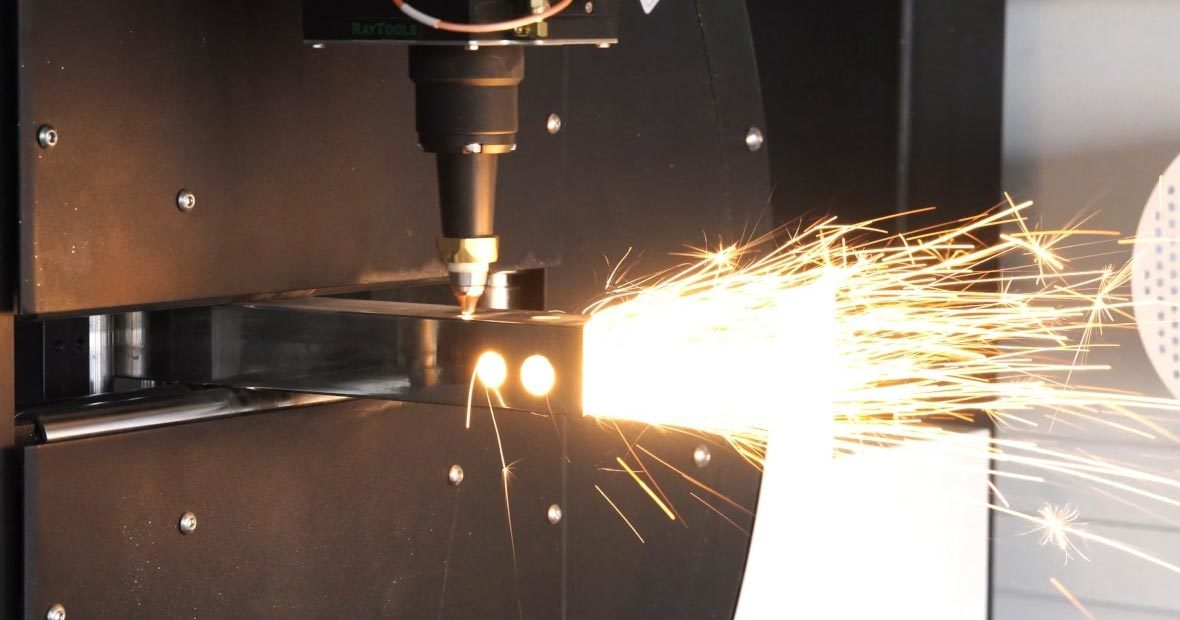
Unmatched Precision and Superior Cut Quality
This is often the most significant draw. Laser cutting utilizes a highly focused beam of light, resulting in:
- Extreme Accuracy: Achieve incredibly tight tolerances, crucial for parts requiring precise fits and complex assemblies.
- Narrow Kerf: The actual cut width (kerf) is minimal, allowing for intricate designs, sharp corners, and less wasted material.
- Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): The heat impact on the surrounding material is significantly less compared to plasma, reducing warping and preserving material integrity, especially on thinner sheets.
- Clean Edges: Laser cuts typically produce smooth, clean edges with minimal dross or burrs, drastically reducing or eliminating the need for secondary finishing processes. This saves time, labor, and cost.
Imagine producing parts that fit perfectly the first time, every time, with an edge quality that requires little to no cleanup – that's the laser advantage.
Speed Where It Matters Most: Boosting Throughput
While plasma cutting can be faster on very thick plates, laser cutting reigns supreme in speed for thin to medium-thickness materials.
- Rapid Cutting on Sheets: For materials commonly used in sheet metal fabrication (up to approx. 10-15mm), laser cutters often significantly outperform plasma in terms of linear cutting speed.
- Faster Processing of Complex Designs: The ability to quickly navigate intricate patterns and small holes without losing precision contributes to overall faster part production.
Increased speed directly translates to higher throughput, shorter lead times, and the ability to take on more jobs, boosting your overall productivity and profitability.
Incredible Versatility: One Machine, Multiple Possibilities
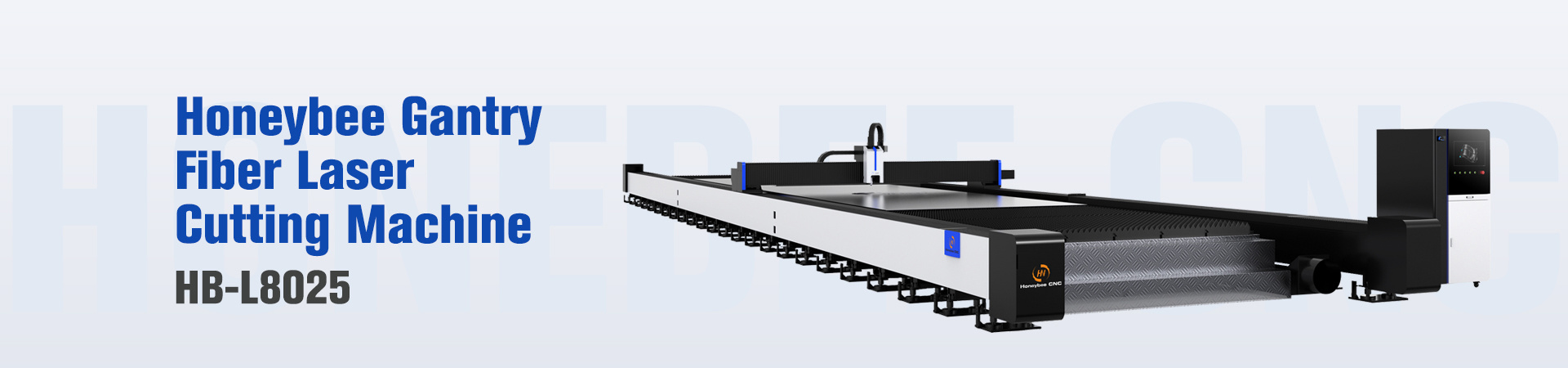
Modern laser cutters, particularly fiber lasers offered under our HoneybeeCNC brand, offer remarkable flexibility:
- Wide Material Range: Efficiently cut various metals including mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Some laser types can even process non-metals.
- Complex Geometry Handling: Easily cut intricate shapes, small holes, sharp angles, and detailed patterns that are challenging or impossible for other thermal cutting methods.
- Non-Contact Process: The laser beam cuts without physical contact, eliminating tool wear and reducing the risk of material distortion due to clamping forces.
This versatility means one machine can handle a broader range of jobs, simplifying your workflow and expanding your business capabilities compared to more specialized equipment.
Enhanced Efficiency: Automation and Reduced Labor
Laser cutting systems are inherently suited for automation and streamlined operation:
- Seamless CNC Integration: Fully integrated with Computer Numerical Control (CNC) for precise, repeatable, and automated cutting based on digital designs.
- Potential for Lights-Out Operation: High reliability and automation capabilities allow for unattended operation in some cases, maximizing machine utilization.
- Reduced Post-Processing: As mentioned, the high cut quality minimizes grinding, deburring, and finishing steps, freeing up labor for other value-added tasks.
Laser vs. Plasma Cutting: A Quick Glance at Key Differences
While plasma cutting has its place, especially for thick conductive materials where budget is a primary concern, comparing key parameters highlights laser's strengths:
|
Feature |
Laser Cutting |
Plasma Cutting |
Advantage Focus for Laser |
|
Precision/Tolerance |
Excellent (Typically ±0.05mm to ±0.1mm) |
Good (Typically ±0.2mm to ±0.5mm+) |
Superior accuracy for complex parts |
|
Cut Edge Quality |
Excellent (Smooth, minimal dross) |
Good (Can have bevel, more dross) |
Reduced need for secondary finishing |
|
Kerf Width |
Very Narrow |
Wider |
Less material waste, finer details possible |
|
Heat Affected Zone |
Minimal |
Larger |
Less material distortion, better integrity |
|
Speed (Thin Metal) |
Very Fast |
Moderate |
Higher throughput on sheet metal |
|
Complexity Handling |
Excellent (Intricate shapes, small holes) |
Good to Moderate |
Ideal for detailed designs |
|
Material Versatility |
High (Various Metals, some Non-Metals) |
Good (Conductive Metals Only) |
Broader application range |
|
Need for Finishing |
Minimal to None |
Often Required |
Saves significant time and labor costs |
Note: Values are typical and can vary based on machine power, model, settings, and material.
Making the Smart Choice for Your Business
While plasma cutting remains a viable option for specific applications (primarily thick plate cutting on a tighter budget), the compelling benefits of laser technology in precision, speed, quality, and versatility often provide a faster return on investment and a significant competitive advantage.